Project Description
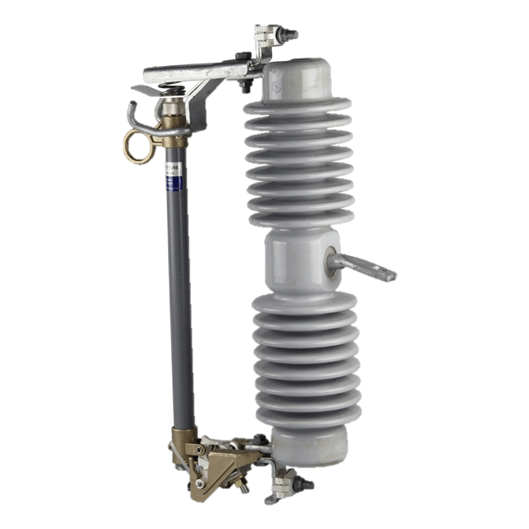
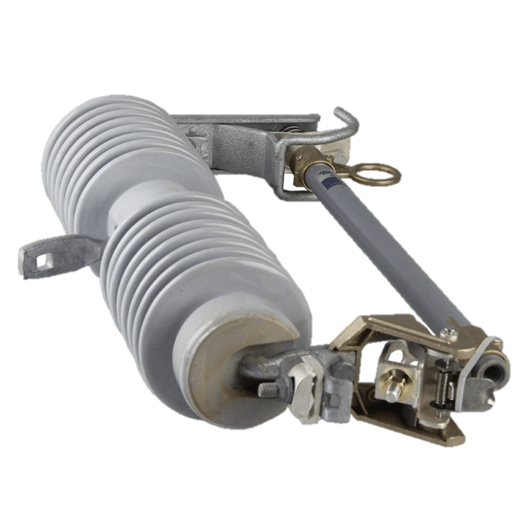
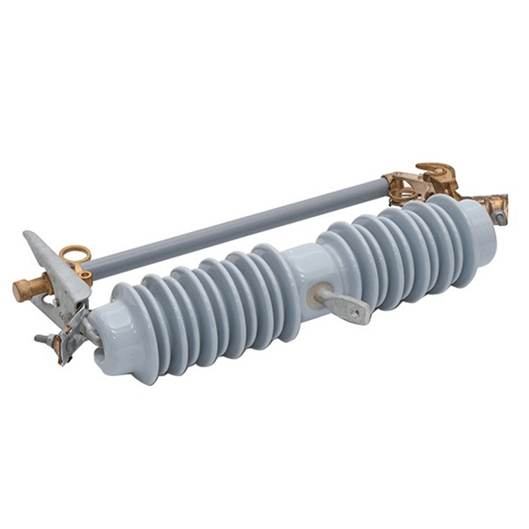
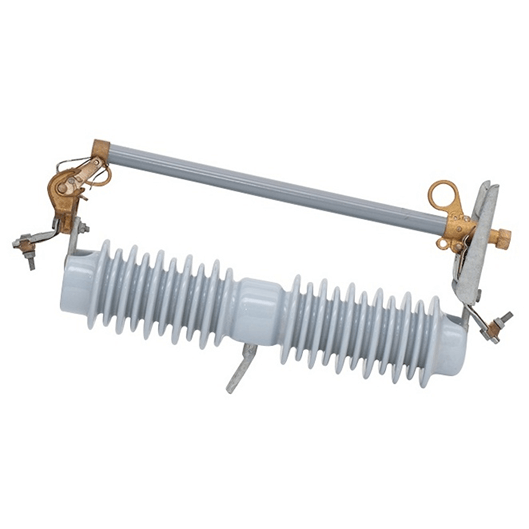
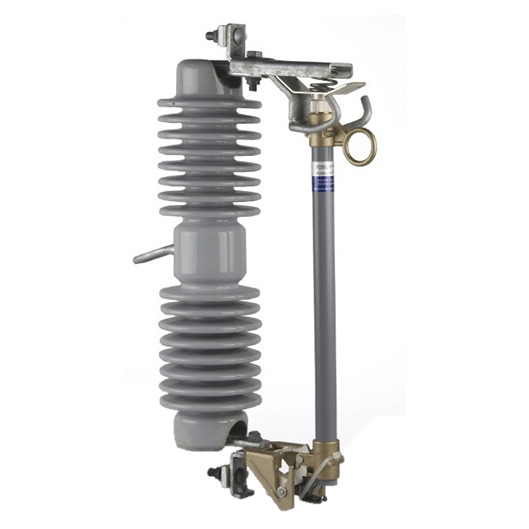
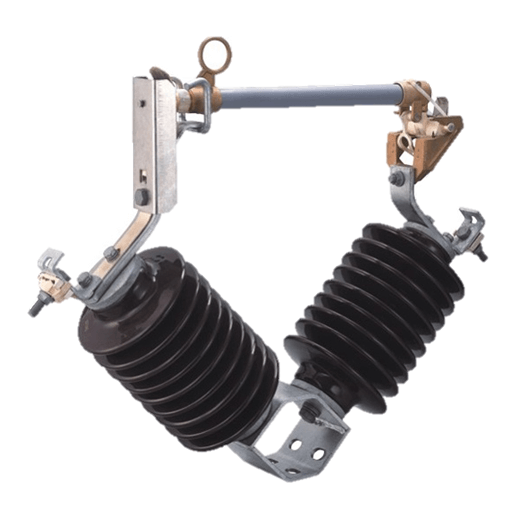
33-36kV Porcelain Drop Out Fuse Cutout
Application of Expulsion Fuse Cutout:
Generally, fuse cut-out contains following parts: (1) Insulator; (2) Metal parts; (3) Fuse tube; (4) Fuse element (link).
Connected with incoming feeder of distribution transformer or distribution lines, high-voltage drop-out fuse cut-out mainly protect transformer or lines form short circuit and overhead, and on/off loading current. Cut out fuse is composed of insulators and fuse tube/carrier. Static contacts are fixed on two sides of insulator support while moving contacts are installed on two ends of fuse tube/carrier. Fuse tube/carrier is composed of inner arc-extinguishing tube, outer phenolic compound paper tube or epoxy glass tube.
Covering rated voltages of 10 to 40.5KV for over current protection, fuse cut-out is divided in two types: Composite (Silicone rubber) type and Porcelain type.
Drop out fuses and load-drop fuses are outdoor high voltage protection appliances. They are installed on the high voltage side of the distribution transformer or on the branch line of the distribution line, used as a short circuit of the transformer and the line, overload protection and cut out load current.
Dropout fuse is composed of two parts: An insulating bracket and a fuse tube. The static contact is installed at two ends of the insulating bracket, the movable contact is installed at both ends of the fuse tube, and the fuse tube is composed of an inner arc extinguishing tube and an outer layer.
It consists of a phenolic paper tube or an epoxy glass tube. The load drop fuse enhances the elastic auxiliary contact and the arc extinguishing cover to divide and combine the load current.
Circuit switching off processes by fuse cut-out is as follow:
In case of any deficiency or problem in main lines, a short connection takes place. This short connection flows in the main lines. As soon as the current passes, the voltage of the main line drops rapidly and reaches to zero. The energy created by current passage of short connection melts the fuse element. At melting status, the temperature of fuse element (link) increases the resistance of fuse (element); and current passage decreases the pressure of both tips of fuse. When the element is melted, the spark arc current passes through the fuse; the current resistance increases quickly. So the pressure increases at both tips of fuse. The extra pressure, which not provided by main line, would be provided by circuit inductivity of trans (e=1 di/dt); and finally this inductivity causes the current to drop zero. It should be mentioned that these processes take place in a few milli-seconds and disconnection of fuses will occur in a few milli-seconds. For example, when 9 amp current passes through a 25 Amp fuse, this current will be cut in 2.7 seconds.
Application environment:
- Ambient temperature: -40 ~ +40℃
- Altitude above sea level: ≤3000m
- Maximum wind speed: ≤35m/s
- Earthquake intensity: ≤8 degrees
| Rated Voltage (KV) |
Rated Current (A) |
Breaking current (A) |
BIL (KV) |
Power frequency withstand voltage (kV) |
Creepage distance (mm) |
Weight (kgs) |
Dimension (cm) |
| 33-36 | 100 | 8000 | 170 | 70 | 720 | 12.5 | 66*37.5*14 |
| 33-36 | 200 | 10000 | 170 | 70 | 720 | 13.0 | 66*37.5*14 |
Video loading, please wait…
Video loading, please wait…
Video loading, please wait…